qPCR Reagents
-
Posted: May 14, 2025Read more »
In cellular and molecular research, the quality and reliability of your reagents are paramount to achieving reproducible and meaningful results. ScienCell offers a selection of high-quality
cell culture reagents designed to support critical steps in your experimental workflows!
-
Posted: May 11, 2025Read more »
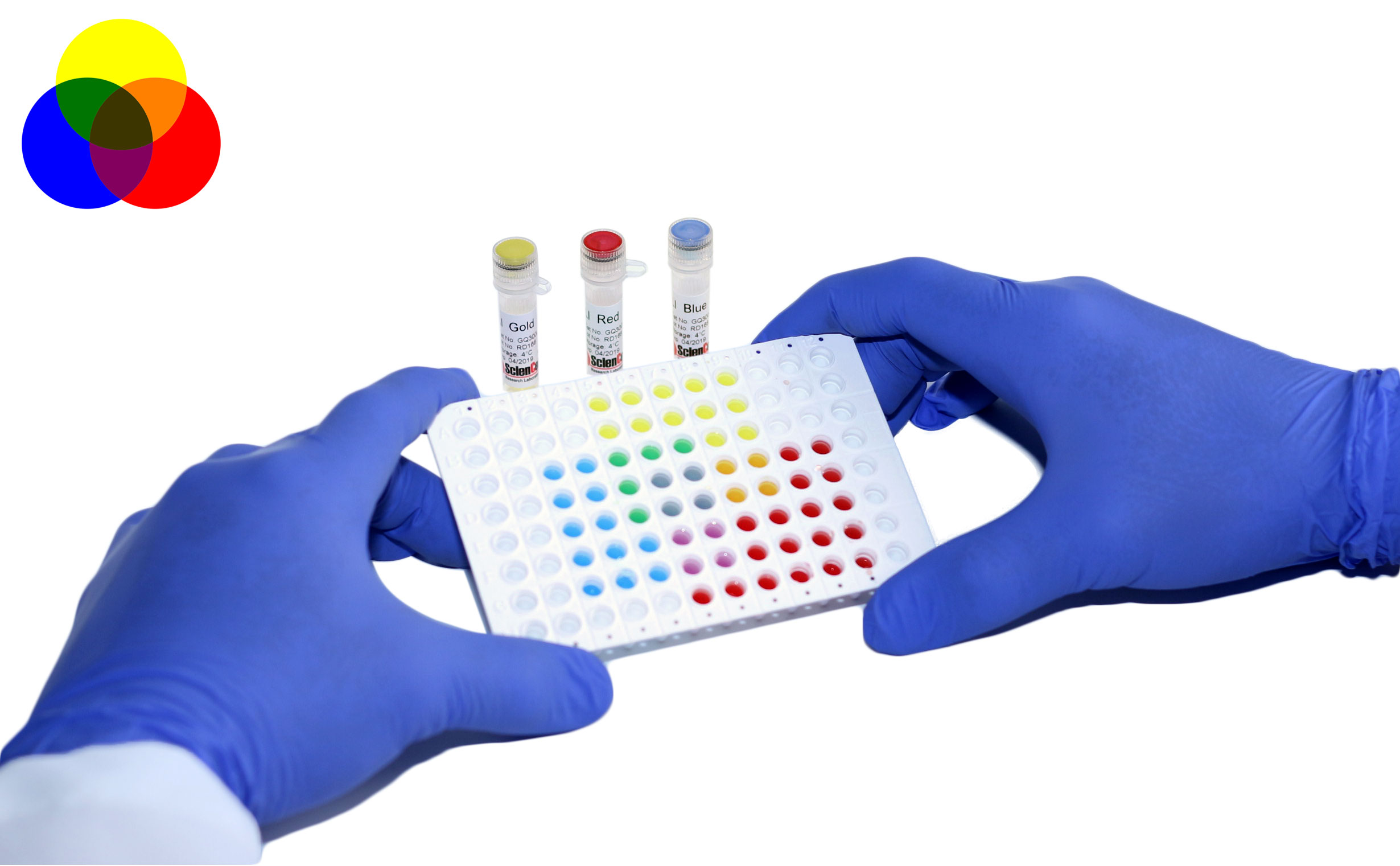
ScienCell’s trusted GoldNStart TaqGreen qPCR Master Mix just got even better. Our latest upgrade features an integrated 2-color tracking system designed to make your qPCR workflow faster, easier, and more accurate—without sacrificing any of the reliability you know and trust.
-
Posted: April 03, 2020Read more »
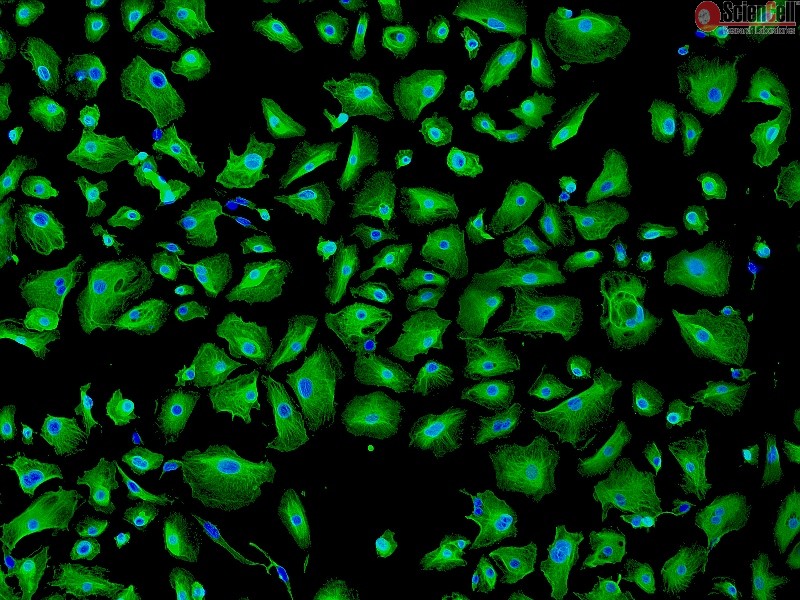
Epithelial cells are the most numerous cells in the lungs and contribute to innate and adaptive immunity. Airway epithelial cells are located in the lower respiratory tract which includes the trachea, bronchi, small airways (bronchioles), and alveoli. Due to their location, airway epithelial cells are
-
Posted: February 09, 2020Read more »
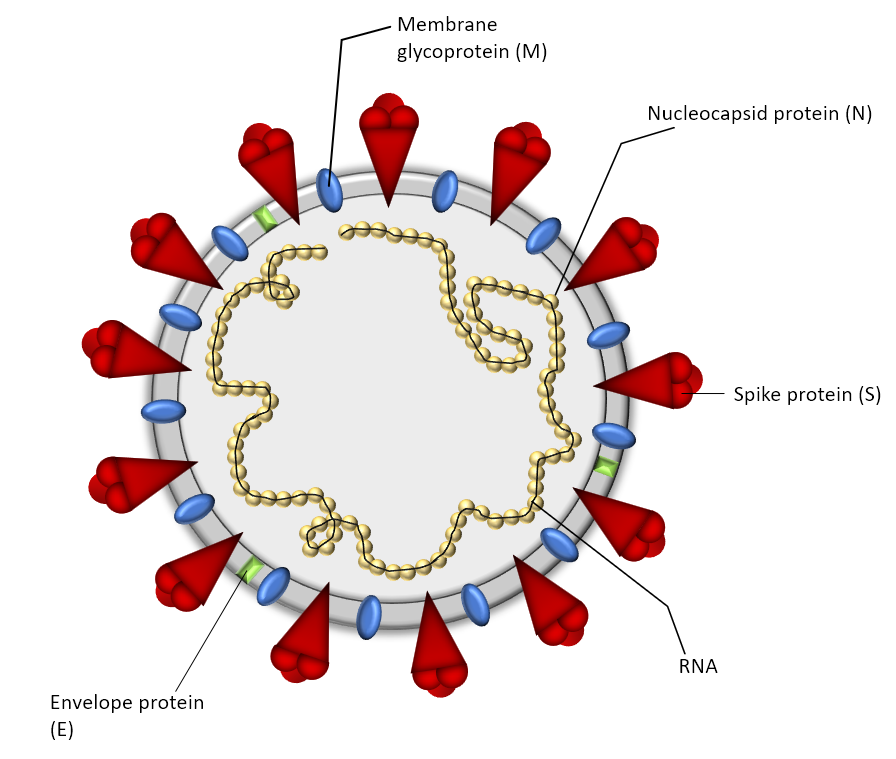
As of April 10, 2020, the number of U.S. SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus cases surpassed 500,000 with a death toll near 19,000. For over a century, coronaviruses were thought to only cause mild illnesses such as the common cold. With the ou or over a century, coronaviruses were thought to only cause mild illnesses
-
Posted: August 28, 2018Read more »
qPCR is a powerful tool for quantification of gene expression levels and copy number variation. Despite the advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS), qPCR still serves as the "gold standard" for gene expression analysis. Due to poor reproducibility and vast lab-to-lab variation, all NGS data requires










.png)
