COVID-19
Welcome to our COVID-19 Blog, where we share research updates, testing resources, and scientific insights related to SARS-CoV-2. Explore the latest findings and tools supporting ongoing studies.
-
Posted: April 30, 2020Read more »
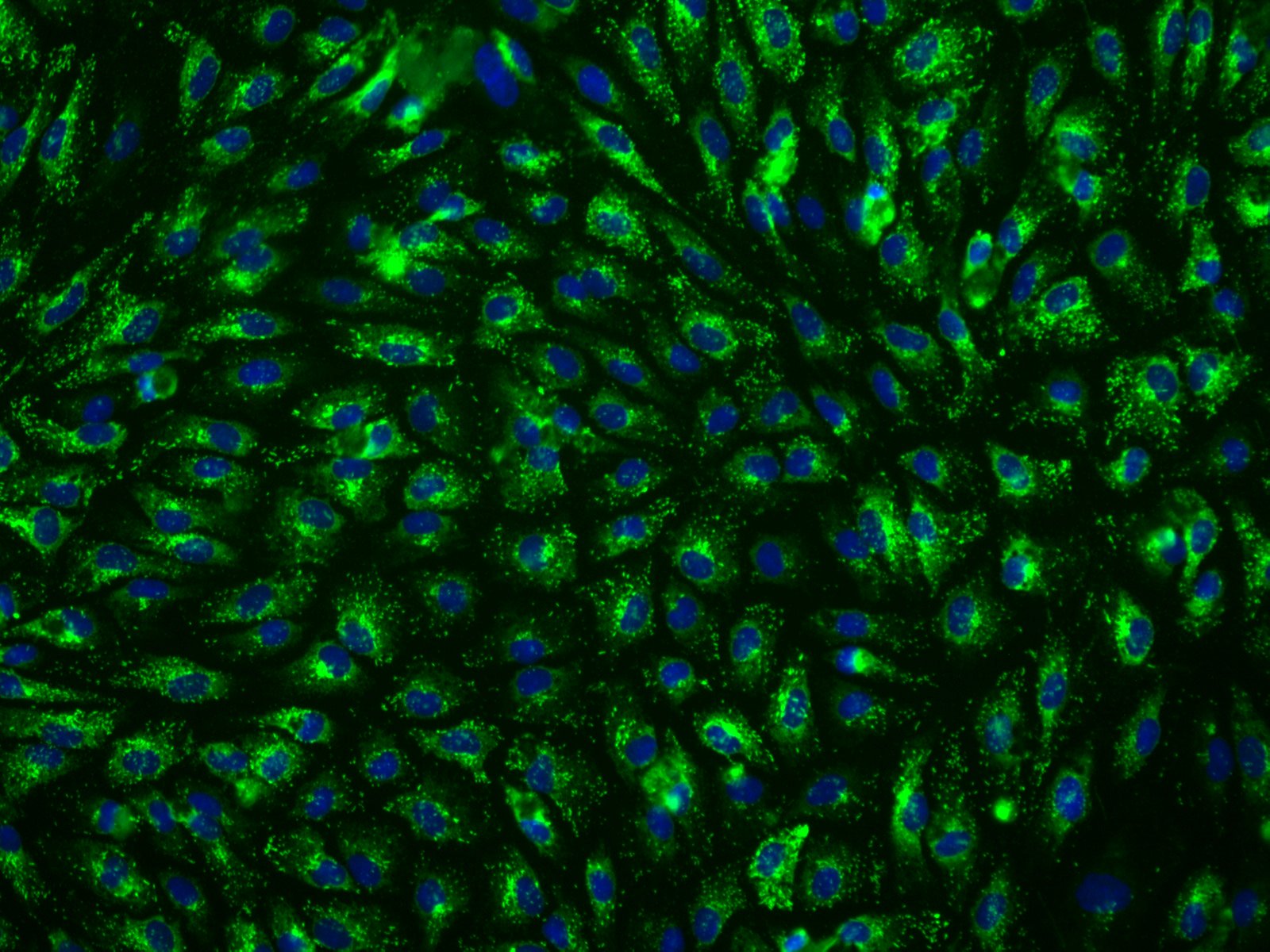
Hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells (HSEC) are fascinating cells that are uniquely adapted to their location in the liver. HSEC are found lining micro-vessels in the liver and are extremely specialized endothelial cells. Structurally and functionally they have distinctive features which include: open
-
Posted: April 20, 2020Read more »
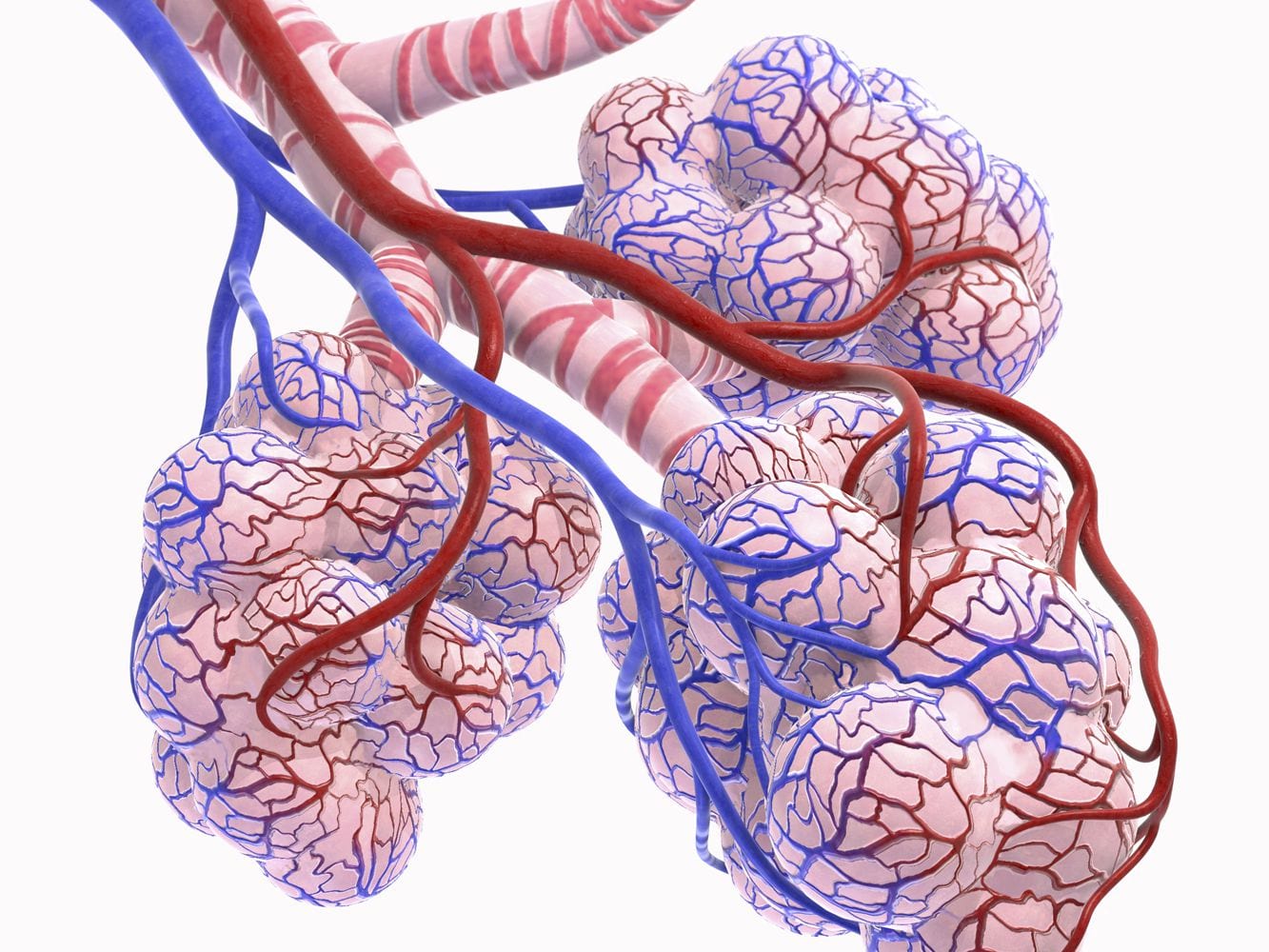
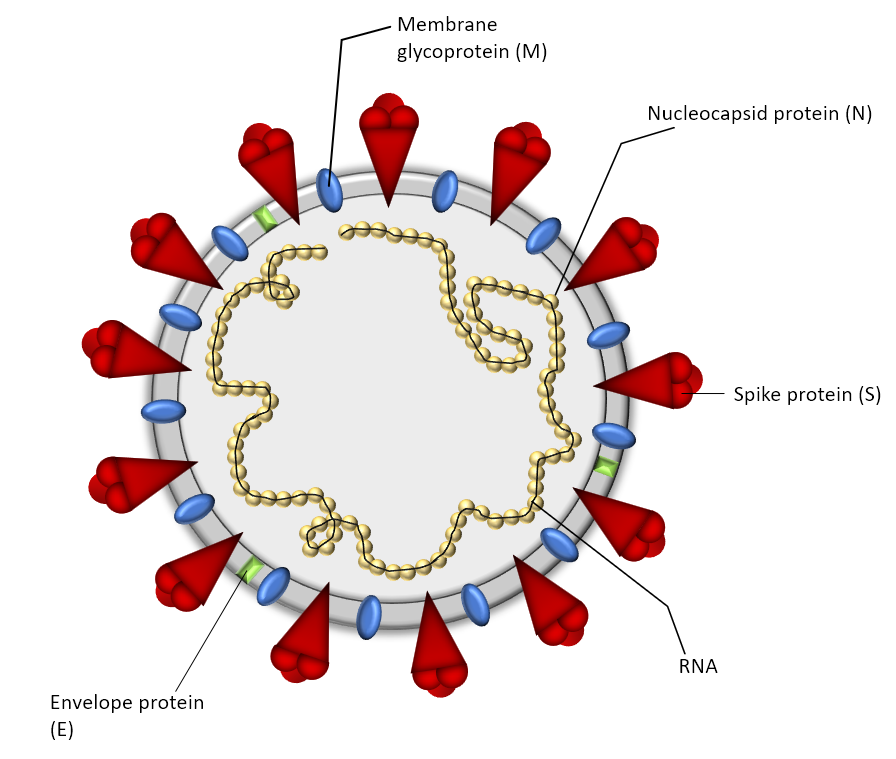
SARS-CoV-2 is the seventh known coronavirus that causes the human disease known as COVID-19. The virus can grow in cells lining the conducting airways and in alveolar epithelial cells. First, the virus generally enters the body through the nose or mouth. From there, the virus travels down into the alveoli
-
Posted: April 03, 2020Read more »
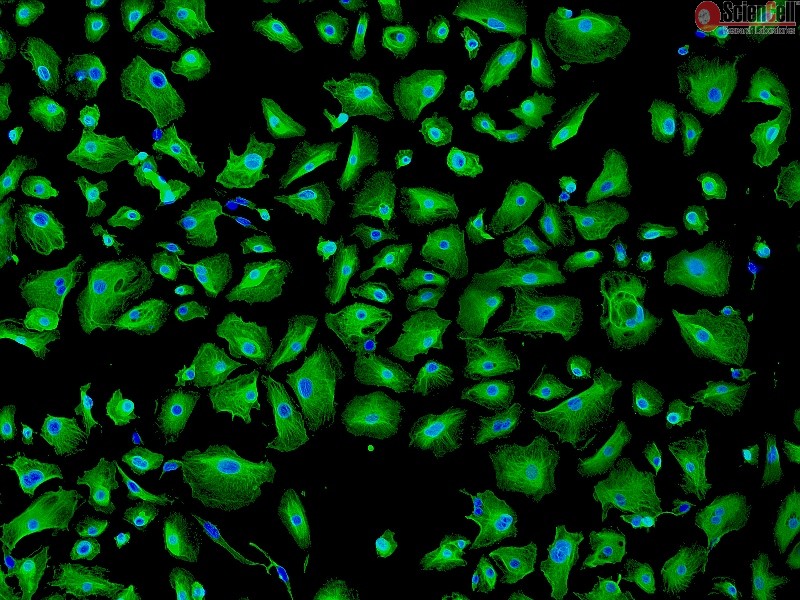
Epithelial cells are the most numerous cells in the lungs and contribute to innate and adaptive immunity. Airway epithelial cells are located in the lower respiratory tract which includes the trachea, bronchi, small airways (bronchioles), and alveoli. Due to their location, airway epithelial cells are
-
Posted: February 09, 2020Read more »
As of April 10, 2020, the number of U.S. SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus cases surpassed 500,000 with a death toll near 19,000. For over a century, coronaviruses were thought to only cause mild illnesses such as the common cold. With the ou or over a century, coronaviruses were thought to only cause mild illnesses