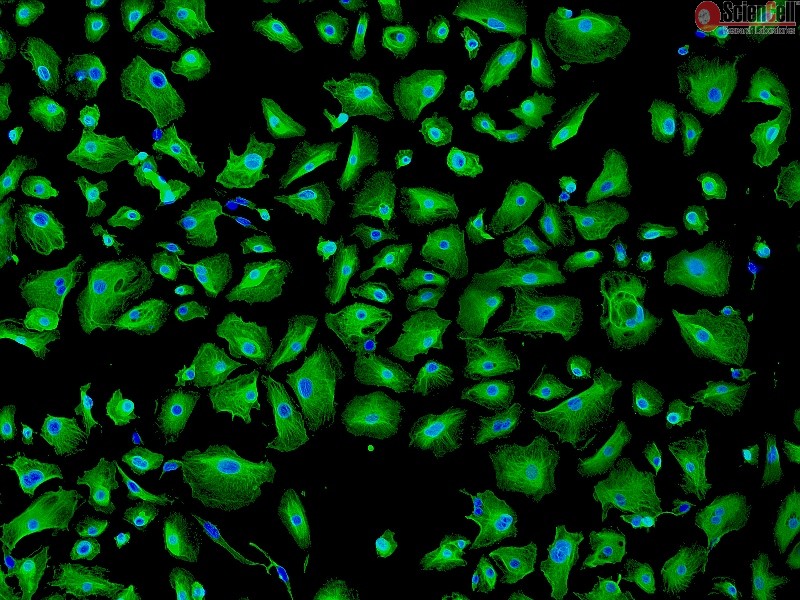
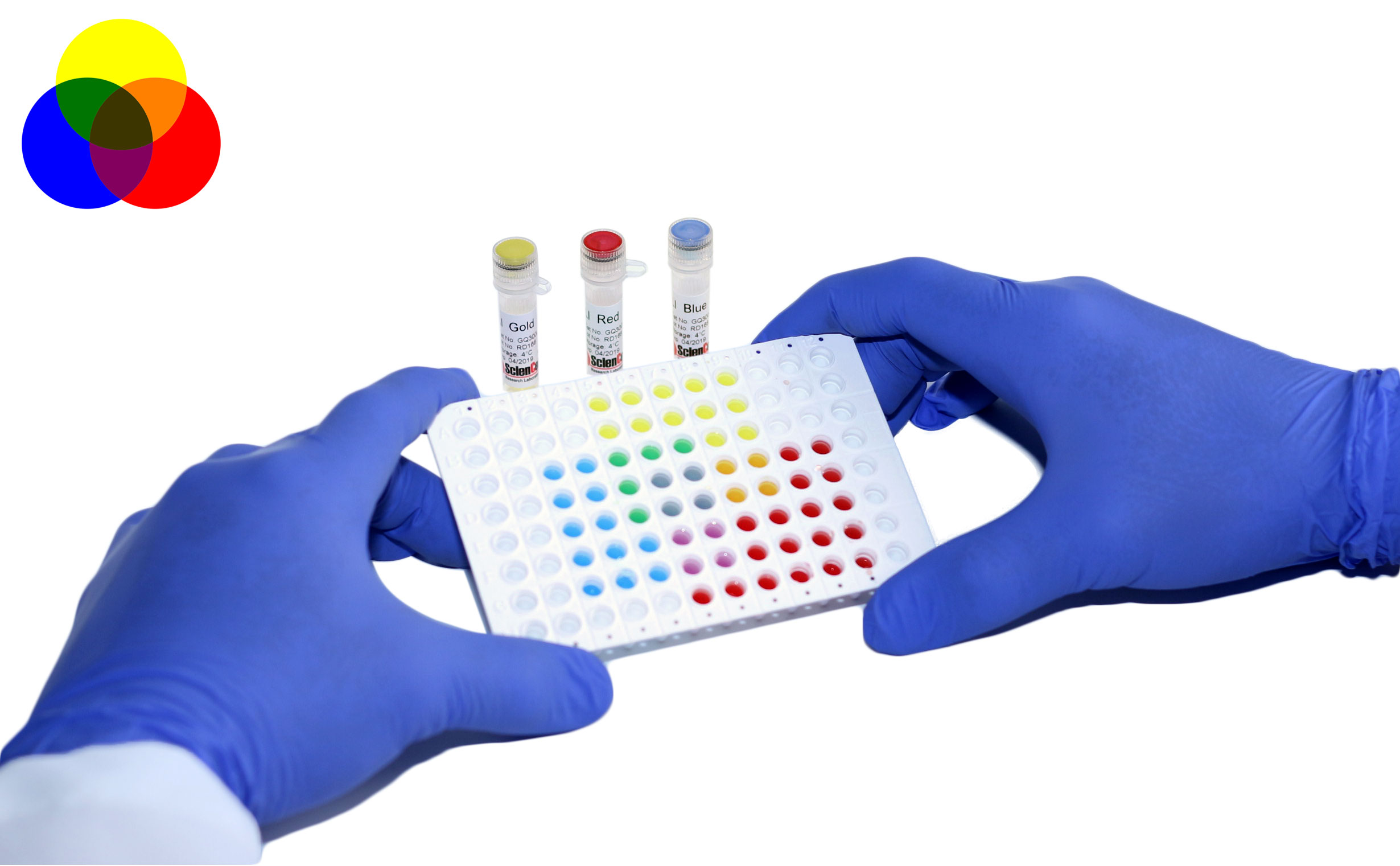
Telomeres protect our chromosomes and shorten with each cell division, a process tied to aging. Telomerase, the enzyme that replenishes these protective caps, is essential for stem cell function and cancer progression. Measuring telomerase activity is critical for understanding aging, cancer, and stem
信息
-
发布: 游行 08, 2026完整阅读 »
-
发布: 二月 03, 2026完整阅读 »Heart Health in Focus: Cardiac Primary Cells for Cardiovascular DiscoveryFebruary marks American Heart Month, an observance dedicated to advancing awareness of cardiovascular health and the critical research needed to prevent and treat heart disease. At ScienCell, we recognize the essential role that
-
发布: 十月 09, 2025完整阅读 »
The Wnt pathway plays a central role in cell signaling, development, and disease, yet studying it often poses technical challenges. Its complexity stems from a tightly regulated network of proteins and receptors that drive processes such as stem cell renewal, tissue regeneration, and cancer progression.
-
发布: 十月 07, 2025完整阅读 »
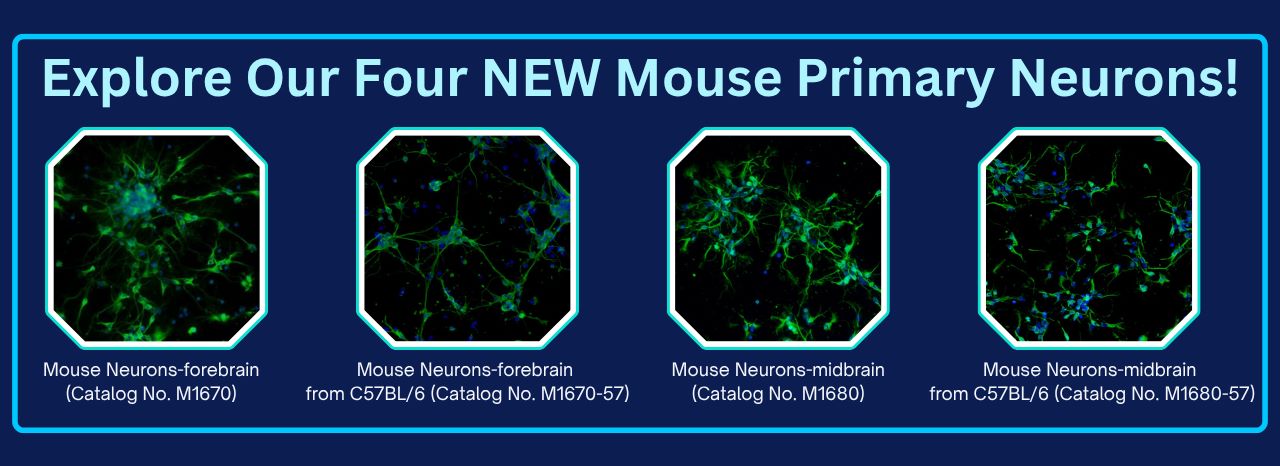
Neurons are the dynamic, anatomically, functionally, and trophically vital units of the brain, responsible for electrochemically transmitting information across the nervous system. While all neurons share common morphological features, their regional specialization is what truly drives brain function.
-
发布: 十月 06, 2025完整阅读 »
We are excited to announce and launch two new products for Wnt/β-catenin signaling research: the TCF/LEF Dual Reporter Vector (TDRV, Catalog No. 9038) and the Luciferase Assay Kit (LAK, Catalog No. 9048).
The TDRV provides the reporter system, and the LAK provides the robust, accurate measurement,
-
发布: 十月 06, 2025完整阅读 »
Highly bioactive, animal-free growth factors and cytokines for iPSC and ESC cell culture
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSC) are a type of pluripotent stem cell derived from adult somatic cells such as skin cells or blood cells, through cellular reprogramming. Embryonic stem cells (ESC) are derived
-
发布: 九月 30, 2025完整阅读 »
Telomeric repeat–containing RNA (TERRA) plays a vital role in telomere biology, influencing telomerase activity, chromosome stability, and cellular aging. Abnormal TERRA expression has been linked to cancer, aging, and age-related diseases. But detecting TERRA has always been a challenge due to:
-
发布: 七月 28, 2025完整阅读 »
At Sciencell, we are committed to providing high-quality tools to support groundbreaking research. This month, we are excited to showcase two powerful proteases: Recombinant Yeast SUMO Protease (Catalog No. MB9018) and Recombinant TEV Protease (Catalog No. MB9028). These reagents are designed to streamline
-
发布: 七月 06, 2025完整阅读 »
Unlock precise control over cellular processes with ScienCell's extensive range of recombinant human proteins. Engineered for stability and biological activity, our products are essential tools for studying cell proliferation, differentiation, tissue development, and disease mechanisms.
Explore our
-
发布: 六月 05, 2025完整阅读 »
Save Time. Reduce Variability. Get Results.
Working with primary cells is essential for biologically relevant data, but sourcing tissues, isolating cells, and extracting high-quality RNA, DNA, or protein can be time-consuming, expensive, and technically demanding.
Our line of cell-derived molecular
-
发布: 可能 27, 2025
-
发布: 可能 26, 2025完整阅读 »
Why Choose Our MSCs? Our Mesenchymal Stem Cells are:
- Multipotent—capable of differentiating into a variety of lineages, such as osteoblasts, chondrocytes, endothelial cells, hepatocyte-like cells, and many more.
- Multiple organ systems—derived from adipose, liver, bone, and the umbilical cord, our MSCs
-
发布: 可能 15, 2025完整阅读 »
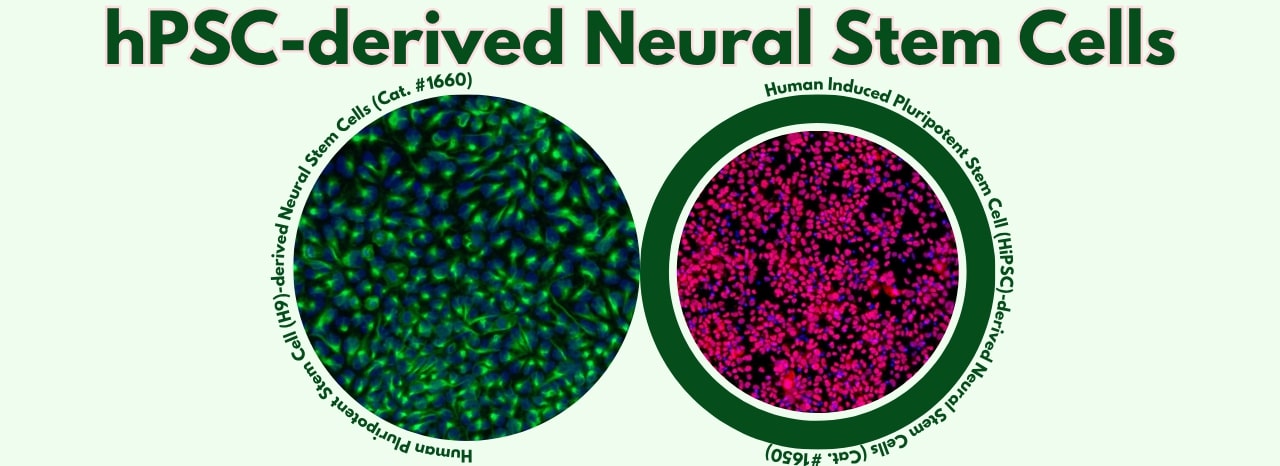
Leading the way in providing advanced tools for life science research, ScienCell Research Laboratories offers high-quality, well-characterized neural stem cell products derived from pluripotent stem cell sources, along with supporting reagents.
These products provide unique advantages for diverse applications,
-
发布: 可能 14, 2025完整阅读 »
In cellular and molecular research, the quality and reliability of your reagents are paramount to achieving reproducible and meaningful results. ScienCell offers a selection of high-quality
cell culture reagents designed to support critical steps in your experimental workflows!
-
发布: 可能 14, 2025完整阅读 »
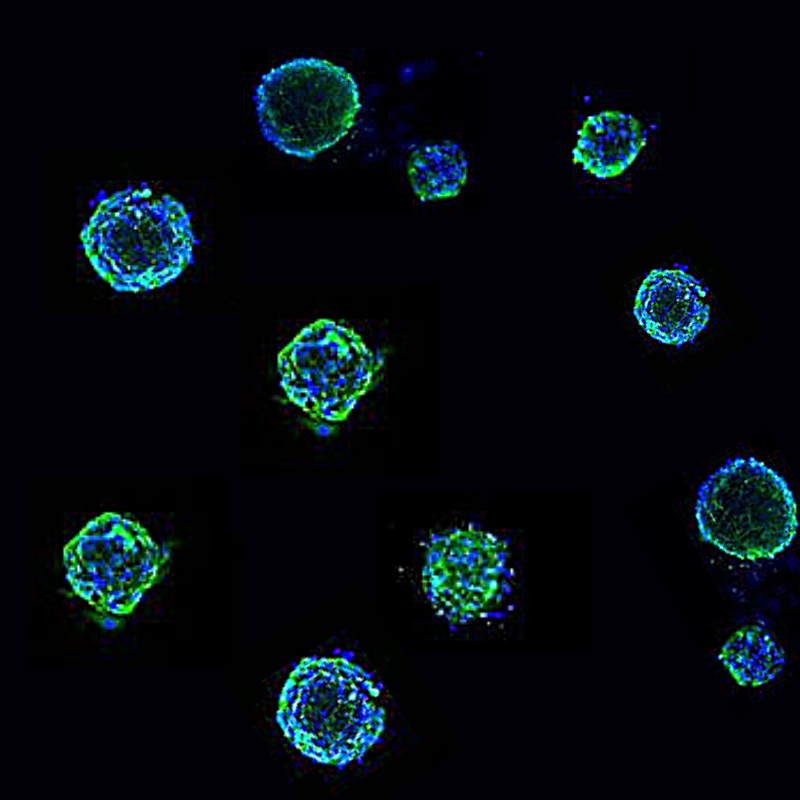
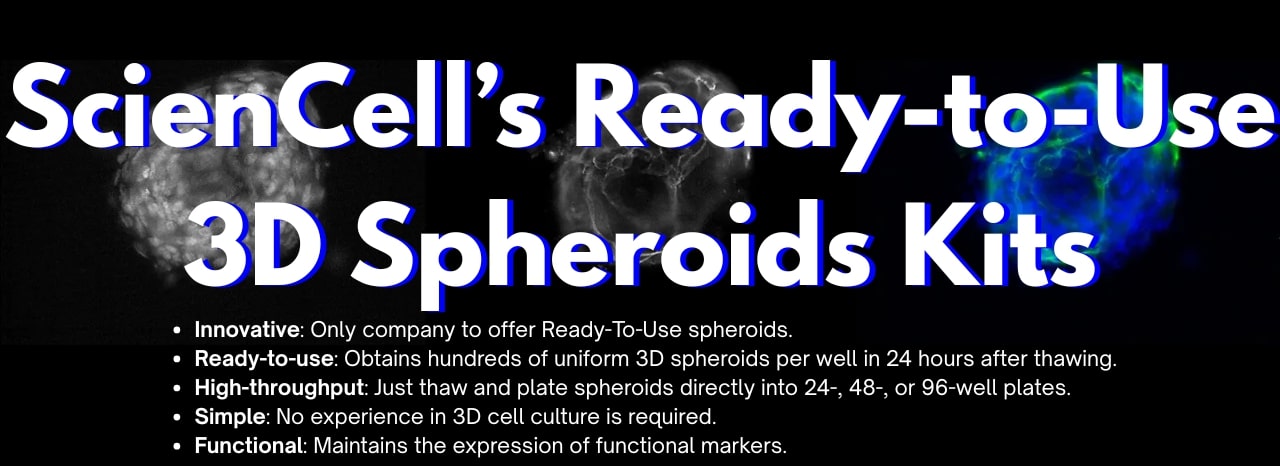
Building and maintaining consistent 3D spheroid models can traditionally involve long and complex workflows sometimes described as tedious and rate limiting.
Our featured ready-to-use 3D spheroid kits address this challenge. These innovative products allow researchers to obtain highly homogenous and
-
发布: 可能 12, 2025完整阅读 »
Achieving physiologically relevant in vitro models is paramount for groundbreaking research. The extracellular matrix (ECM) plays a critical role in cell behavior, influencing everything from adhesion and spreading to growth and differentiation.
To provide your cells with the optimal environment,
-
发布: 可能 11, 2025完整阅读 »
ScienCell’s trusted GoldNStart TaqGreen qPCR Master Mix just got even better. Our latest upgrade features an integrated 2-color tracking system designed to make your qPCR workflow faster, easier, and more accurate—without sacrificing any of the reliability you know and trust.
-
发布: 可能 08, 2025完整阅读 »
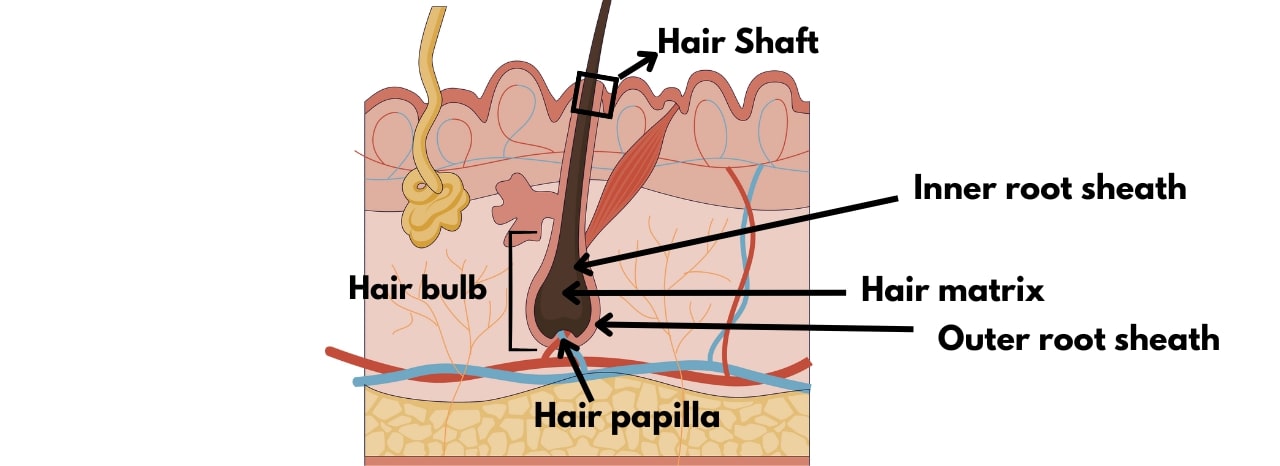
As the demand for advanced models in regenerative medicine and hair restoration therapies grows, so does the need for reliable, physiologically relevant primary cells.
ScienCell Research Laboratories offers a suite of human hair follicle cell types to empower your research — each isolated from human
-
发布: 可能 06, 2025完整阅读 »
ScienCell Research Laboratories offers over 5,400 individual primer sets for human and mouse gene expression analysis, plus our GeneQuery™ qPCR Array Kits for high-throughput studies. Each lyophilized primer set is pre-validated and provides enough material for 100 x 20µL qPCR reactions—perfect for
-
发布: 可能 01, 2025完整阅读 »
ScienCell Research Laboratories offers a robust foundation for skeletal muscle research with our high-purity Human Skeletal Muscle Cells (HSkMC, Cat. #3500). These cells are isolated from adult human skeletal muscle and cryopreserved at passage one to ensure optimal viability and physiological relevance. -
发布: 四月 30, 2025完整阅读 »
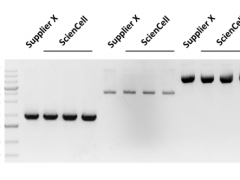
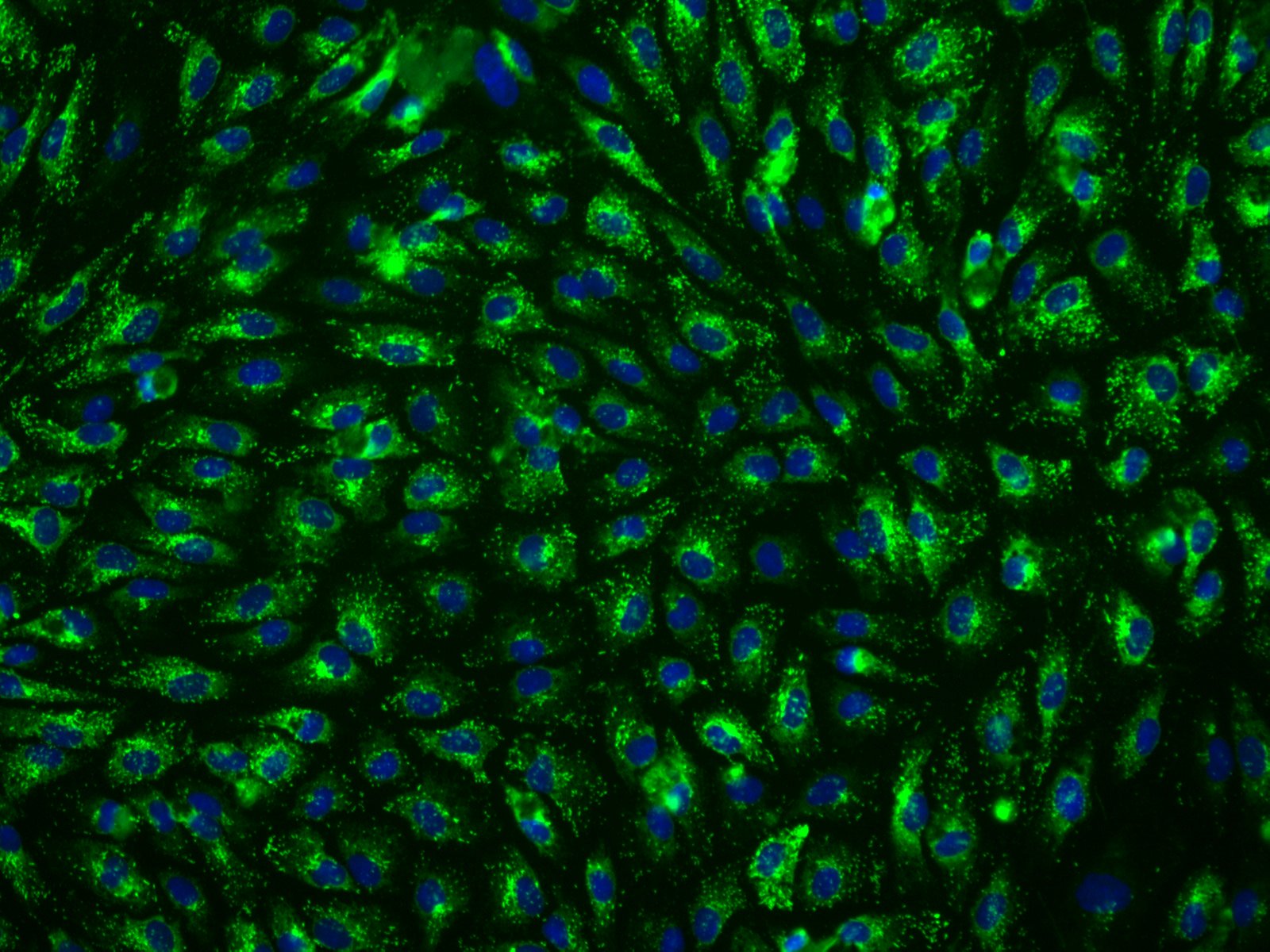
Dermal fibroblasts, derived from the embryonic mesoderm are fundamental components of the skin's dermis layer. Their versatility and ease of culture make them extensively used in cellular and molecular studies. Due to their durability, they are also suitable for a variety of manipulations, such as gene
-
发布: 十月 30, 2024分类: Information完整阅读 »
Interleukins (IL) are a group of cytokines initially believed to be expressed solely by leukocytes, but they are now known to be produced by a variety of cells of the body. These proteins are crucial for activating and differentiating immune cells and play roles in cell proliferation, maturation, migration,
-
发布: 十一月 12, 2020分类: Information完整阅读 »
Isolation of high-quality nucleic acids from biological material is a key factor in successful molecular biology research. While approaches vary, most methods aim to do the following: (1) disrupt the cellular structure, (2) denature and inactivate other macromolecules (e.g., proteins, enzymes, etc.),
-
发布: 四月 30, 2020完整阅读 »
Hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells (HSEC) are fascinating cells that are uniquely adapted to their location in the liver. HSEC are found lining micro-vessels in the liver and are extremely specialized endothelial cells. Structurally and functionally they have distinctive features which include: open
-
发布: 四月 03, 2020完整阅读 »
Epithelial cells are the most numerous cells in the lungs and contribute to innate and adaptive immunity. Airway epithelial cells are located in the lower respiratory tract which includes the trachea, bronchi, small airways (bronchioles), and alveoli. Due to their location, airway epithelial cells are
-
发布: 二月 09, 2020完整阅读 »
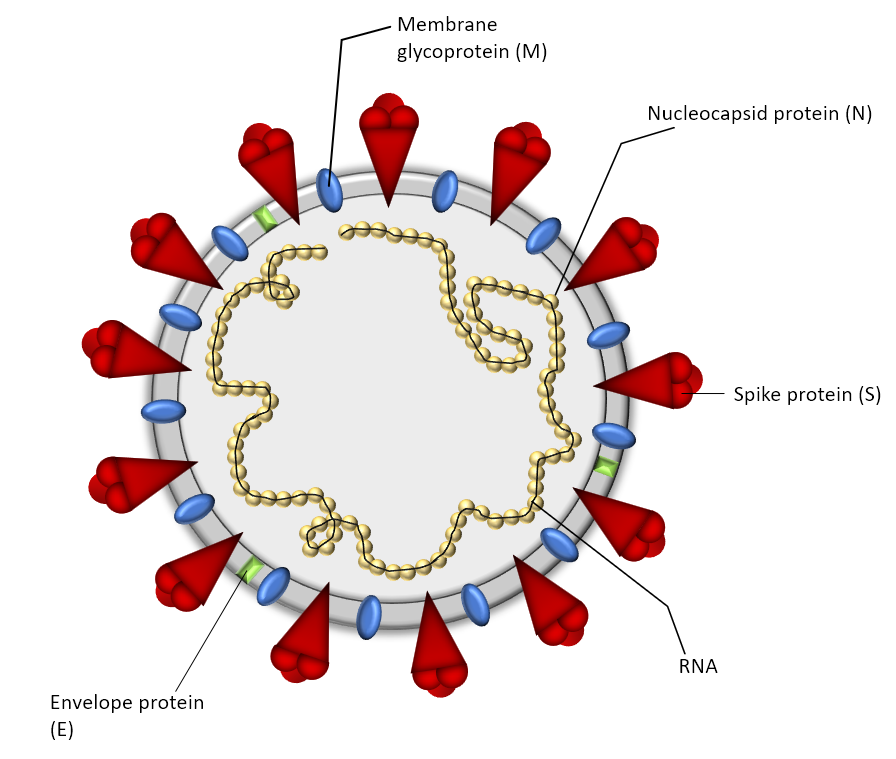
As of April 10, 2020, the number of U.S. SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus cases surpassed 500,000 with a death toll near 19,000. For over a century, coronaviruses were thought to only cause mild illnesses such as the common cold. With the ou or over a century, coronaviruses were thought to only cause mild illnesses
-
完整阅读 »
Traditional 2D cultures have been used widely over the past decades to study cell biology, molecular biology and conduct translation research such as drug discovery. Cells in 2D culture, however, are forced to adopt a planar morphology and maintain cellular interactions only in lateral directions, altering
-
发布: 六月 09, 2019完整阅读 »
Hepatic stellate cells have recently gained a great deal of attention regarding their contribution to the progression of diseases such as liver fibrosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and hepatocellular carcinoma. They are mesenchymal cells that are located between sinusoidal endothelial cells
-
发布: 二月 11, 2019完整阅读 »
ScienCell’s wide assortment of cell culture media is in liquid form and includes Specialty, Classical & Supplement varieties. Each product is designed for optimal nutrition and growth of primary cells. ScienCell’s cell culture media is manufactured and tested to ensure a high standard of quality and
-
发布: 八月 28, 2018完整阅读 »
qPCR is a powerful tool for quantification of gene expression levels and copy number variation. Despite the advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS), qPCR still serves as the "gold standard" for gene expression analysis. Due to poor reproducibility and vast lab-to-lab variation, all NGS data requires
-
发布: 可能 30, 2018完整阅读 »
When working with primary cells, it is important to remember that they are not cell lines and should be treated with care. At ScienCell, we specialize in primary cell culture and we are very familiar with the common problems researchers encounter when culturing them. We have compiled a list with 13
-
完整阅读 »
Cancer immunotherapy is one promising cancer treatment option whereby the host's own immune system is used to treat cancer. The therapy works by either stimulating certain immune activities, or counteracting cancer cell signals that suppress immune responses. Cancer immunotherapy has progressed significantly
-
发布: 游行 13, 2018完整阅读 »Mesenchymal Stem Cell Medium-animal component free (Cat. #7521)
For decades, Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) has been a vital supplement for the successful culture of a diverse range of cell types. FBS is an undefined, complex source of growth factors, hormones, lipids, attachment factors, and trace elements.
-
完整阅读 »
Aging and Telomere Length Quantification by qPCR
Aging is a time-dependent decline of the body’s functional capabilities and is an inevitable course of life (as shown in the image below, extracted from the Wall Street Journal). The rate of aging though is highly variable among individuals. When evaluating
-
完整阅读 »
Neuronal cell lines are commonly used for in vitro neurobiology studies because they are more easily transfected compared to primary neurons and they proliferate, whereas primary neurons do not. Neuronal cell lines can be induced to differentiate into neuron-like cells, where they express neuronal markers
-
完整阅读 »
The 2017 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Jeffrey C Hall, Michael Rosbash, and Michael W Young for research that established key mechanistic principles on how circadian rhythms are regulated. Circadian rhythms are endogenous oscillations adjusted to changing external cues and driven
-
发布: 九月 20, 2017完整阅读 »
Next generation sequencing (NGS), such as Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) and RNA-Sequencing (RNA-Seq), provides a high throughput approach for DNA sequencing and gene expression analysis. It is rapidly advancing our knowledge on almost all aspects of genetic research and shedding light on how individual
-
发布: 游行 26, 2017
-
发布: 八月 17, 2016完整阅读 »
After watching displays of astounding athletic prowess in the 2016 Olympics, I was inspired to take a closer look at the science behind exercise training, recovery, and injury with a focus on the importance of blood vessels during exercise.
Let’s start with some basic training: Why are blood vessels
-
发布: 二月 09, 2016分类: Information完整阅读 »
American Heart Month Sponsor: The American Heart Association (http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/)
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men and women in the United States. Every year, 1 in 4 deaths are caused by heart disease.
The good news? Heart disease can often be prevented when people
-
发布: 十一月 01, 2015分类: Information完整阅读 »
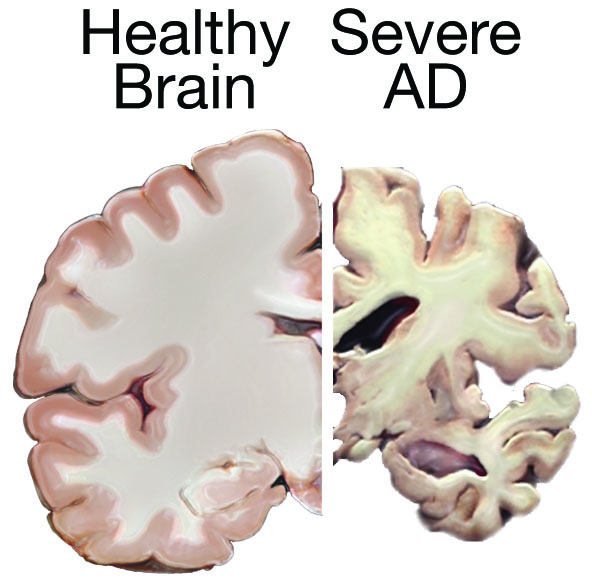
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) affects almost 44 million people worldwide. The disease typically begins with memory difficulties followed by trouble thinking, reasoning and processing emotions. The cause of AD is not well understood, but there appear to be two forms: 90% of patients have a late-onset sporadic






.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)