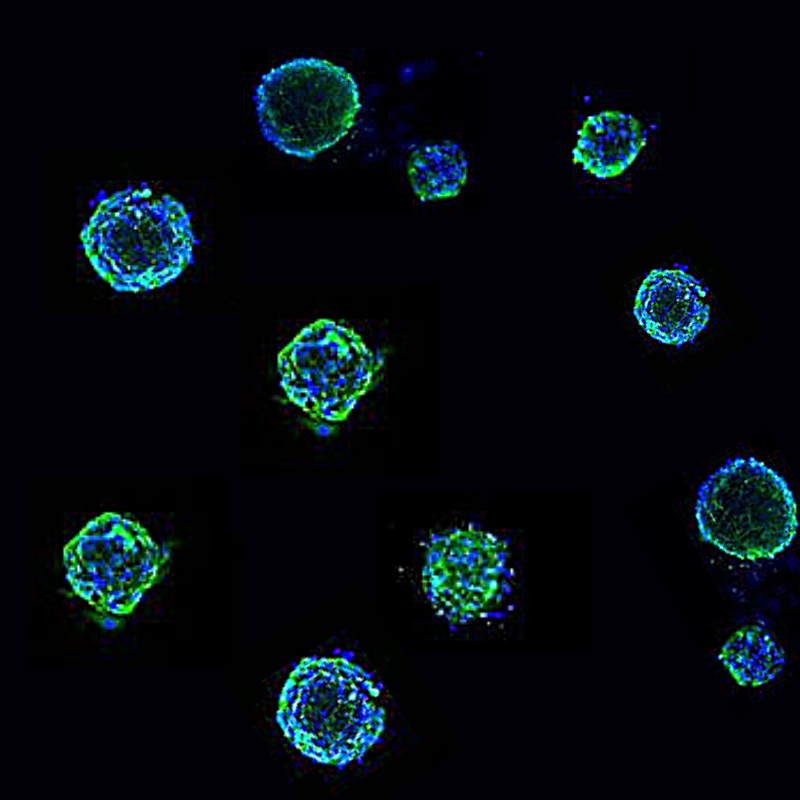
Building and maintaining consistent 3D spheroid models can traditionally involve long and complex workflows sometimes described as tedious and rate limiting.
Our featured ready-to-use 3D spheroid kits address this challenge. These innovative products allow researchers to obtain highly homogenous and